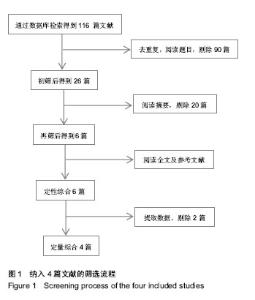
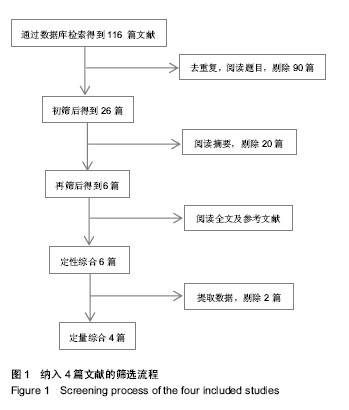
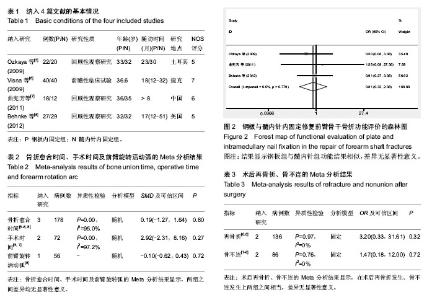
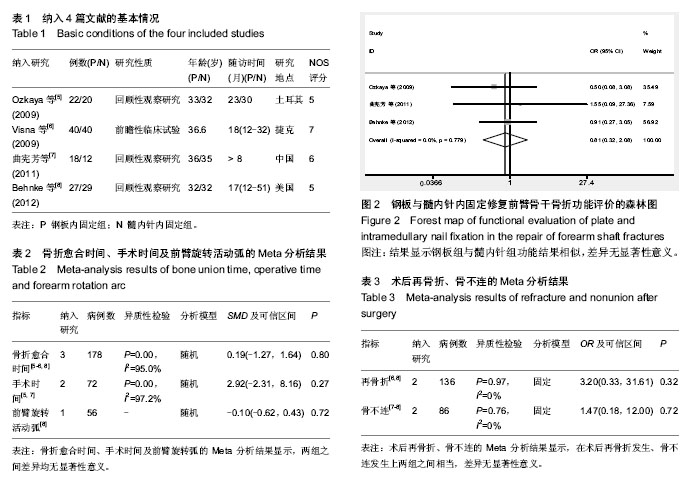
| [1] 张长青,曾炳芳,唐明杰,等.应用前臂交锁髓内钉治疗前臂骨折[J]. 中华手外科杂志, 2004,20(1):18-20.
[2] Chung KC, Spilson SV. The frequency and epidemiology of hand and forearm fractures in the united states: abstract. J Hand Surg[Am]. 2001;26:908-915.
[3] Dymond IW. The treatment of isolated fractures of the distal ulna. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1984; 66:408-410.
[4] Jones DB Jr, Kakar S. Adult diaphyseal forearm fractures: intramedullary nail versus plate fixation. J Hand Surg Am. 2011;36(7):1216-1219.
[5] Ozkaya U, Kilic A, Ozdogan U, et al.Comparison between locked intramedullary nailing and plate osteosynthesis in the management of adult forearm fractures. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2009;43(1):14-20.
[6] Visna P, Vlcek M, Valcha M, et al. [Management of diaphyseal forearm fractures using LCP angle- stable fixation devices and intramedullary nailing]. Rozhl Chir. 2009;88(12):708-715.
[7] 曲宪芳,赵宇,刘书茂,等. AO接骨板与Sanatmetal髓内钉固定治疗尺桡骨单节段双骨折的比较[J].中国骨与关节外科, 2011, 4(6):460-463.
[8] Behnke NM, Redjal HR, Nguyen VT, et al. Internal fixation of diaphyseal fractures of the forearm: a retrospective comparison of hybrid fixation versus dual plating. J Orthop Trauma. 2012;26(11):611-616.
[9] 马晓春.不同治疗方法对尺桡骨干双骨折前臂功能的影响研究[J].临床医学工程, 2012,19(5):738-739.
[10] Schemitsch EH, Jones D, Henley MB, et al. A comparison of malreduction after plate and intramedullary nail fixation of forearm fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 1995;9(1):8-16.
[11] Wells GA, Shea B, O'Connell D, et al. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses [EB/OL]. http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp
[12] Chapman MW, Gordon JE, Zissimos AG. Compression-plate fixation of acute fractures of the diaphyses of the radius and ulna. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1989;71(2):159-169.
[13] Anderson LD, Sisk D, Tooms RE, et al. Compression-plate fixation in acute diaphyseal fractures of the radius and ulna. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1975;57(3):287-297.
[14] Schemitsch EH, Richards RR. The effect of malunion on functional outcome after plate fixation of fractures of both bones of the forearm in adults. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1992; 74(7):1068-1078.
[15] Mih AD, Cooney WP, Idler RS, et al. Long-term follow-up of forearm bone diaphyseal plating. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994; (299):256-258.
[16] Trlica J, Pocepcov I, Koci J, et al. [True/Flex intramedullary nailing for forearm shaft fractures. Long-term results]. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2012;79(4):347-354.
[17] Lee YH, Lee SK, Chung MS, et al. Interlocking contoured intramedullary nail fixation for selected diaphyseal fractures of the forearm in adults. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90(9): 1891-1898.
[18] Rehman S, Sokunbi G. Intramedullary fixation of forearm fractures. Hand Clin. 2010;26(3):391-401. |